Study: Brain-inspired electronic system could vastly reduce AI’s carbon footprint
Extremely energy-efficient artificial intelligence is now closer to reality after a study by UCL researchers found a way to improve the accuracy of a brain-inspired computing system.
The system, which uses memristors to create artificial...
Study: Receptor makes mice strong and slim
Increasing abdominal girth and shrinking muscles are two common side effects of aging. Researchers at the University of Bonn have discovered a receptor in mice that regulates both effects. Experiments with human cell cultures...
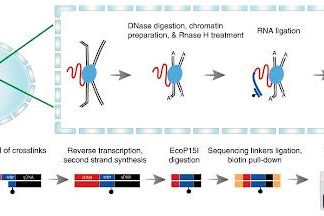
Study: New technology will show how RNA regulates gene activity
The discovery of a huge number of long non-protein coding RNAs, aka lncRNAs, in the mammalian genome was a major surprise of the recent large-scale genomics projects. An international team including a bioinformatician from...
Study: Seizures during menstrual cycle linked to drug-resistant epilepsy
More frequent seizures during the menstrual cycle in women with genetic generalized epilepsy have been linked for the first time to drug-resistant epilepsy, when anti-seizure medications don't work, according to a Rutgers coauthored study...
Study: Re-engineering antibodies for COVID-19
With millions of COVID-19 cases reported across the globe, people are turning to antibody tests to find out whether they have been exposed to the coronavirus that causes the disease. But what are antibodies?...
Study: Brain discovery suggests source of lifelong behavioral issues
UVA neuroscientists have discovered that an unexpected form of cellular cleanup takes place in developing brains. If this process goes wrong -- happening too little or too much -- it can cause permanent changes...
Study: Color-coded biosensor illuminates in real time how viruses attack hosts
Infectious viruses come in many shapes and sizes and use slightly different attack mechanisms to make humans and animals sick. But all viruses share something in common: They can only do damage by replicating...
Report: Community factors influence how long you’ll live
While lifestyle choices and genetics go a long way toward predicting longevity, a new study shows that certain community characteristics also play important roles. American communities with more fast food restaurants, a larger share...
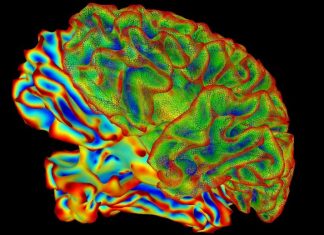
Report: Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease through Single-cell Analysis
The average human brain is the most complicated structure on Earth. Weighing in at three pounds, this amazing organ controls all of the body’s functions, manages interactions with the outside world, stores and retrieves...
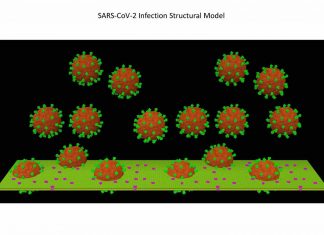
Study: Smoking increases SARS-CoV-2 receptors in the lung
New research from CSHL scientists suggests that cigarette smoke spurs the lungs to make more ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2), the protein that the coronavirus responsible for COVID-19 grabs and uses to enter human cells....