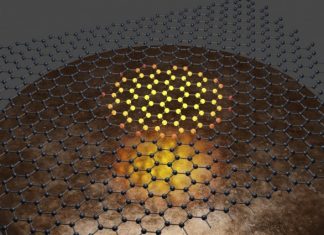
Study: Sensor with 100,000 times higher sensitivity could bolster thermal imaging
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Army-funded research developed a new microwave radiation sensor with 100,000 times higher sensitivity than currently available commercial sensors. Researchers said better detection of microwave radiation will enable improved thermal...
Study: Why writing by hand makes kids smarter
Professor Audrey van der Meer at NTNU believes that national guidelines should be put into place to ensure that children receive at least a minimum of handwriting training.
Results from several studies have shown that...
Study: New tool shows main highways of disease development
As people get older they often jump from disease to disease and carry the burden of more chronic diseases at once. But is there a system in the way diseases follow each other? Danish...
Study: Coral’s resilience to warming may depend on iron
How well corals respond to climate change could depend in part on the already scarce amount of iron available in their environment, according to a new study led by Penn State researchers. The study...
Study: New fire containment research addresses risk and safety
As 2020 has shown, wildfire frequency, size and severity is threatening communities and natural resources across the western U.S. As a result, there is a high demand for decision-making to mitigate risk, improve firefighter...
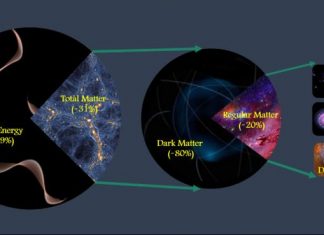
Researchers precisely measure total amount of matter in the universe
A top goal in cosmology is to precisely measure the total amount of matter in the universe, a daunting exercise for even the most mathematically proficient. A team led by scientists at the University...
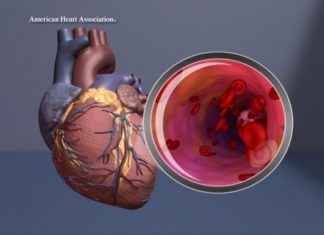
Study: New abdominal aortic aneurysm genes identified, could help pinpoint those at risk
A veteran's study identified more than a dozen genes associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) that could be used to better identify people at risk for the often-deadly condition, according to new research published...
Scientists highlight the impacts of logjams in river restoration projects
Researchers at MIT have modeled how engineered and natural wood jams change river water levels, enabling an assessment of the trade-offs in flood risk and habitat creation for river restoration projects.
In a recent paper...
New Study: Choanozoan and picozoan marine protists are probably virus eaters
Viruses occur in astronomic numbers everywhere on Earth, from the atmosphere to the deepest ocean. Surprisingly, considering the abundance and nutrient-richness of viruses, no organisms are known to use them as food. In Frontiers...
Study: Simpler models may be better for determining some climate risk
Typically, computer models of climate become more and more complex as researchers strive to capture more details of our Earth's system, but according to a team of Penn State researchers, to assess risks, less...